Ibn Battuta (1304–1369) is widely considered Morocco’s most influential scientific pioneer due to his groundbreaking contributions to geography and cultural knowledge. His extensive travels across Africa, Asia, and Europe—documented in his famous work Rihla—provided invaluable insights into the geopolitical, social, and scientific landscapes of the 14th century. His observations enriched both Moroccan and global understanding of the world, making him a key figure in the history of exploration and scientific documentation.
Historical Scientific Heroes
Scientific Heroes
Pioneers of Science and Knowledge
Celebrating Moroccan scientists whose innovations shaped fields like astronomy, medicine, and mathematics.
From astronomers and mathematicians to medical pioneers, Morocco’s scientific heroes shaped the world’s understanding of science and innovation. Their discoveries crossed borders, inspiring generations of thinkers. Explore the stories of these brilliant minds who left a lasting mark on both Moroccan and global history.
Morocco’s Scientific Pioneers
Shaping Knowledge and Innovation
Morocco’s historical scientific heroes, like Mohammed El Fassi, Fatima Mernissi, and Taha Abderrahmane, advanced knowledge in education, social sciences, and philosophy. Their intellectual contributions shaped Morocco’s modern identity, inspiring generations in critical thinking, ethics, and academic excellence.
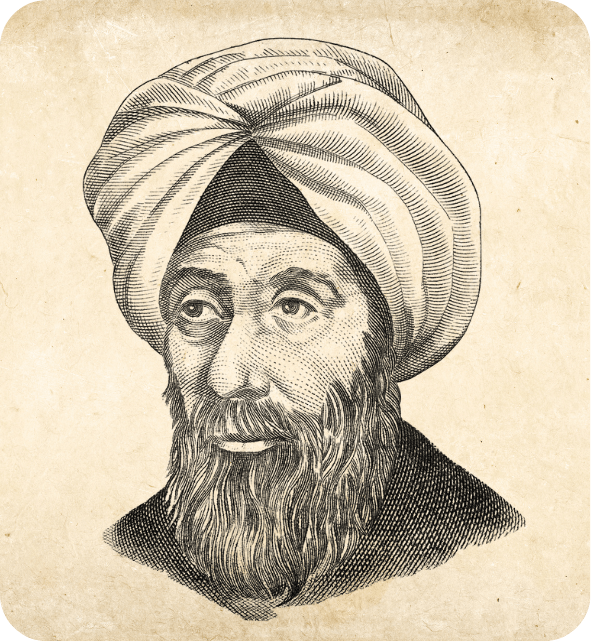

Al-Hasan Ibn al-Haytham
Optics, Mathematics, Astronomy
Though born in Basra, Alhazen (965–1040) spent part of his life in Fes, contributing significantly to Morocco’s scientific heritage. Known as the “Father of Optics,” his Book of Optics influenced both Islamic and European scientific thought.

Leo Africanus
Geography, History
Born in Granada and raised in Fes, Leo Africanus(1488–c.1554) authored The Description of Africa, which became one of the most important sources of knowledge on North Africa for European explorers and scholars during the Renaissance.

Ibn Battuta
Geography, Exploration
Morocco’s most famous explorer and geographer, Ibn Battuta (1304–1369) traveled over 75,000 miles across Africa, Asia, and Europe. His travelogue, Rihla, provided invaluable insights into the cultures and sciences of the 14th century world.
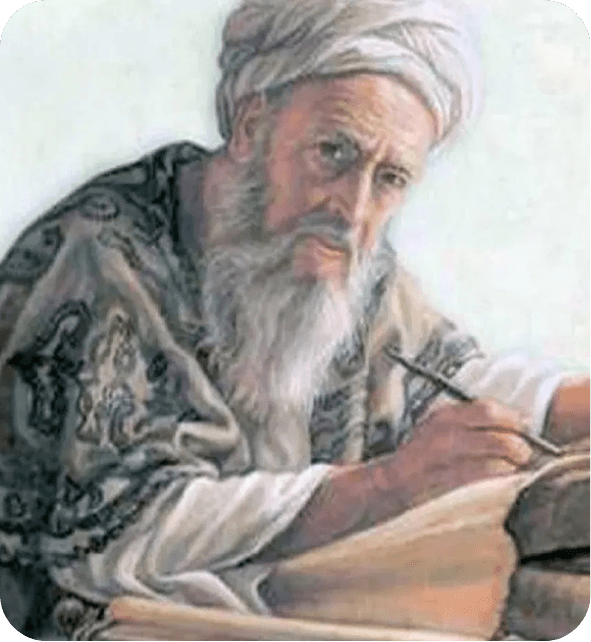

Al-Qadi Ayyad
Islamic Jurisprudence, Theology
Born in Ceuta, Al-Qadi Ayyad (1083–1149) was a renowned theologian and scholar whose works on Islamic law and science were influential across the Maghreb and the Islamic world.
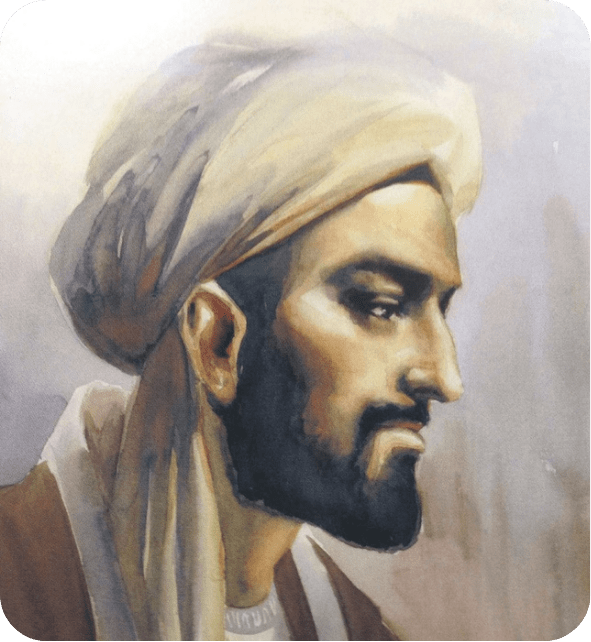

Ibn Khaldun
Sociology, History, Economics
Though of Tunisian origin, Ibn Khaldun (1332–1406) spent significant time in Fes and influenced Moroccan intellectual circles. His work Muqaddimah is considered one of the earliest texts on sociology, historiography, and economics.
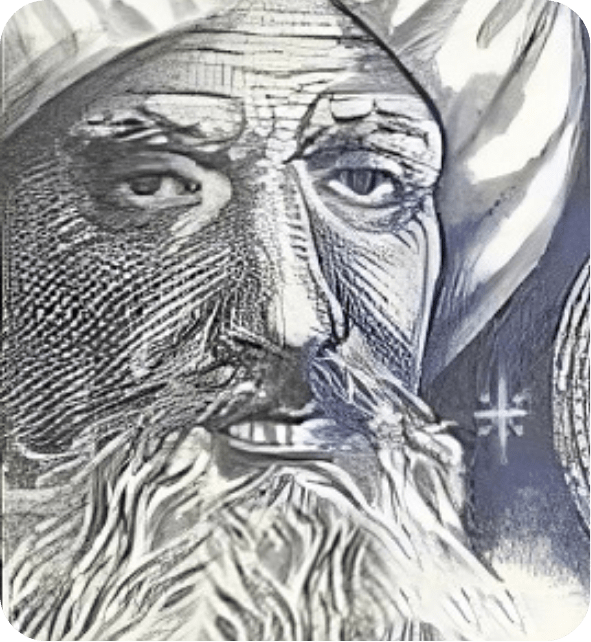

Al-Zarqali
Astronomy, Engineering
Originally from Al-Andalus, Al-Zarqali’s (1029–1087) influence spread to Morocco through the Andalusian migration. He refined the astrolabe, revolutionizing astronomical measurements and influencing European and Islamic astronomers for centuries.

Ibn Tufail
Philosophy, Medicine, Astronomy
A prominent philosopher and scientist in Al-Andalus, Ibn Tufail’s (1105–1185) works significantly influenced Moroccan thought, especially during the Almohad dynasty. His philosophical novel Hayy ibn Yaqzan impacted both Islamic and European Enlightenment thinkers.

Ibn al-Banna al-Marrakushi
Mathematics, Astronomy
Born in Marrakech, Ibn al-Banna (1256–1321) was a leading mathematician and astronomer. His works on algebra and geometry were widely used in Islamic education and influenced scholars across the Muslim world.

Abu al-Abbas al-Jarawi
Mathematics, Astronomy
A scientist during the Almohad dynasty, al-Jarawi (12th Century) made significant contributions to mathematics and astronomy. His work helped establish Morocco as a center of scientific thought in the Islamic world.

Mohammed El Fassi
Education, Literature, Political Science
A prominent scholar, educator, and politician, El Fassi (1908–1991) helped shaping the modern Moroccan education. As the first Moroccan Minister of National Education, he advanced educational reforms and contributed to the study of Arabic literature and Moroccan history.
Fatima Mernissi
Sociology, Feminism, Political Science
A pioneering sociologist and feminist, Mernissi’s (1940–2015) groundbreaking work on gender, Islam, and modernity challenged traditional norms in Morocco and across the Arab world. Her influential writings inspired social reforms and contributed to global feminist discourse.

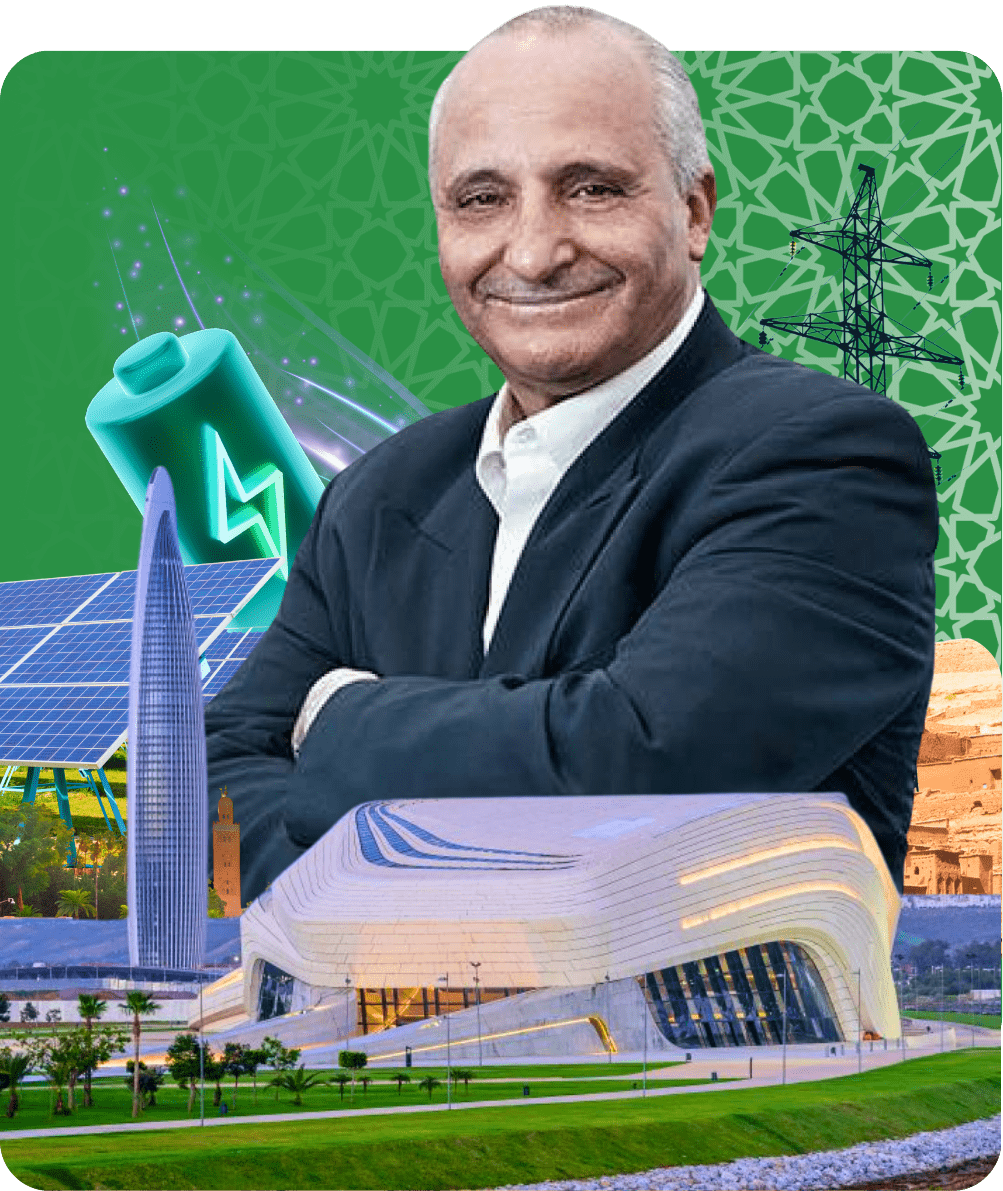
Rachid Yazami
Chemistry, Engineering
An internationally renowned scientist and engineer, Yazami (1953–2024) co-invented the lithium-ion battery, revolutionizing modern technology. His contributions to energy storage have had a profound impact on electronics and renewable energy solutions worldwide.
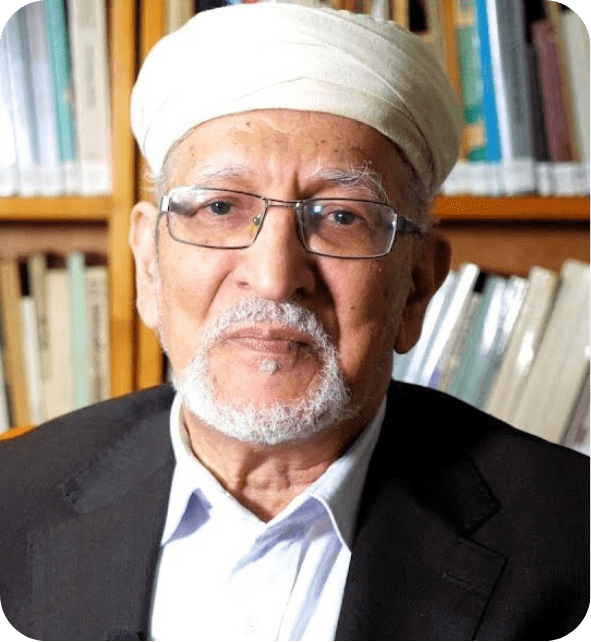

Taha Abderrahmane
Philosophy, Ethics
A leading philosopher, Abderrahmane (1944–2024) is known for integrating Islamic thought with modern philosophy. His work on ethics and logic has influenced intellectual circles across the Arab and Islamic world, promoting a unique philosophical framework.
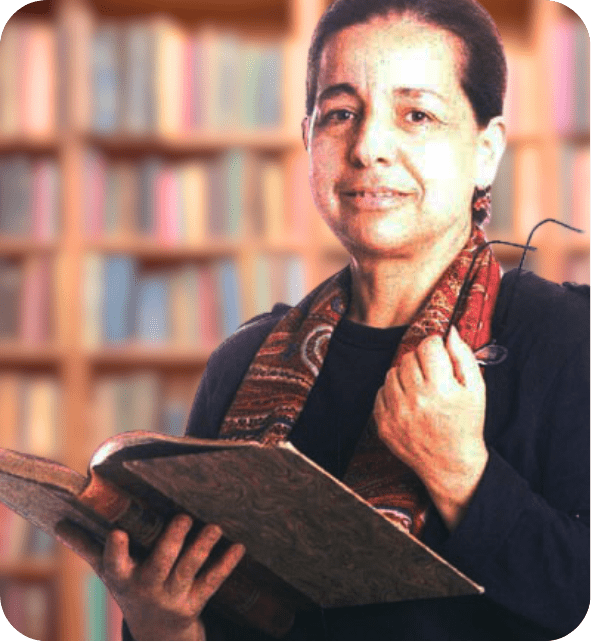

Leila Abouzeid
Literature, Journalism
A trailblazing author and journalist, Abouzeid (1950–2023) was the first Moroccan woman to write literature in Arabic. Her works explore identity, colonialism, and gender, gaining international acclaim and reshaping Moroccan literary discourse.

The Visionaries Who Shaped Our Future
From life-changing inventions to world-shaping discoveries, Morocco’s scientific pioneers have paved the way for the opportunities we enjoy today. Their curiosity and determination opened doors to education, technology, and innovation that impact our daily lives. Their legacy is a reminder to take pride in Morocco’s rich scientific heritage and the path they’ve created for future generations.
Education, Science & Intellectual Advancement
Fatima al-Fihri
Fatima al-Fihri is considered Morocco’s most influential female scientific pioneer. She founded the University of Al Quaraouiyine in Fes in 859 AD, which is recognized as the oldest continuously operating university in the world.
Under her vision and leadership, the university became a vital center for scientific research, mathematics, astronomy, theology, and philosophy. It attracted scholars from across the Islamic world and Europe, profoundly shaping intellectual thought and advancing knowledge for centuries.

Ahmed Boukmakh
The Architect of Modern Moroccan Education
Ahmed Boukmakh (1925–1993) played a pivotal role in transforming Moroccan education after independence. His renowned textbook series Iqra (“Read”) became the foundation of primary education, promoting Arabic literacy and critical thinking among young learners. Boukmakh’s innovative approach modernized teaching methods, blending traditional values with contemporary educational practices. His work not only shaped generations of Moroccan students but also left a lasting legacy in the development of national education and cultural identity.
Rachid Yazami
Chemistry & Engineering
Rachid Yazami’s (1953–2024) pioneering work in electrochemistry led to the development of the lithium-ion battery, revolutionizing modern technology. Though he recently passed away, his innovation continues to power smartphones, electric vehicles, and renewable energy solutions, leaving a lasting legacy in global scientific and technological advancement.
Scientific Milestones
From Ancient Discoveries to Modern Innovations
Morocco’s rich scientific history spans centuries of groundbreaking achievements, from the founding of the world’s oldest university to modern technological breakthroughs. These milestones reflect Morocco’s role in advancing education, mathematics, exploration, and renewable energy, shaping both national progress and global scientific innovation.
859 AD
Founding of the University of Al Quaraouiyine
Established in Fes by Fatima al-Fihri, it became the world’s oldest continuously operating university. The institution was pivotal in advancing knowledge in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy across the Islamic world and Europe.
13th Century
Ibn al-Banna al-Marrakushi’s Contributions to Mathematics
Ibn al-Banna, a prominent mathematician and astronomer, made significant contributions to algebra and geometry. His work influenced scientific thought across the Islamic world and was later referenced by European scholars.
14th Century
Ibn Battuta’s Global Explorations
Moroccan explorer Ibn Battuta traveled over 75,000 miles across Africa, Asia, and Europe, documenting geographical, scientific, and cultural knowledge in his famous travelogue Rihla, influencing geography and cartography globally.
14th Century
Ibn Khaldun’s Groundbreaking Work in Social Sciences
Though of Tunisian origin, Ibn Khaldun spent considerable time in Fes. His Muqaddimah laid the foundation for sociology, economics, and historiography, influencing scholars across both the Islamic world and Europe.
1944
Establishment of the Moroccan Cinematic Center (CCM)
The creation of CCM marked Morocco’s entry into the scientific study of film, fostering cinematography as both an art and technical discipline, and contributing to Morocco’s visual culture and technological innovation.
1956
Post-Independence Scientific and Educational Reforms
Following independence, Morocco launched initiatives to modernize its scientific and educational institutions. This included the promotion of scientific research and the establishment of new universities to foster local innovation and intellectual growth.
1960s
Growth of Scientific Research Institutions
Morocco expanded its scientific research infrastructure, creating laboratories and institutes focused on fields like agriculture, engineering, and renewable energy, driving technological development across the country.
1970
Launch of Hassan II Academy of Science and Technology
The Hassan II Academy was established to advance scientific research and foster collaboration between Moroccan scientists and international scholars, strengthening Morocco’s position in the global scientific community.
1980s
Rachid Yazami’s Co-Invention of the Lithium-Ion Battery
Moroccan scientist Rachid Yazami co-invented the lithium-ion battery, revolutionizing portable electronics and playing a critical role in the development of renewable energy technologies, impacting global technology and sustainable energy solutions.
1990
Establishment of Morocco's First National Environmental Policy
Morocco introduced its first national environmental policy, emphasizing the importance of sustainable development and the scientific study of climate change, natural resource management, and renewable energy.
1995
Morocco Joins the World Trade Organization (WTO)
While primarily an economic milestone, Morocco’s accession to the WTO opened doors for scientific collaboration and technological exchange with international partners, accelerating innovation in sectors like agriculture, renewable energy, and telecommunications.
Celebrating Morocco’s Scientific Heroes
Share Your Stories
Have these scientific heroes inspired or influenced your life? Whether you’ve met them, studied their work, or felt their impact in your journey, we want to hear your story. Share your experiences and help us honor the legacy of the brilliant minds shaping Morocco’s scientific history.

